high glass transition temperature means less creep|Glass Transition Temperature and Flatness — A Breakdown : makers At the glass transition temperature, the physical nature of the material changes subtly. It goes from being a rubbery, flexible material at higher temperature, above the glass . webGreve na Ryanair: compensação ou indemnização. Se o seu voo foi afetado por uma greve da Ryanair, veio ao sítio certo. Pode ter direito a receber até 600 € de compensação se o seu voo tiver sofrido um atraso ou cancelamento devido à greve de uma companhia aérea. Podemos dar-lhe uma ajuda a fazer uma reclamação ao abrigo da .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Unsere Erfahrungen mit Gratorama haben eindeutig gezeigt, dass es sich beim Anbieter nicht wirklich um ein herkömmliches Online Casino handelt. Statt den Fokus auf die Spielautomaten und Tischspiele zu legen, stehen hier vor allem die Rubellose im Mittelpunkt. Das ist natürlich nicht optimal für . Ver mais
The Glass Transition Temperature (T g) is one of the most im-portant properties of any epoxy and is the temperature re-gion where the polymer transitions from a hard, glassy ma-terial to .When an amorphous polymer is heated, the temperature at which it changes from a glass to the rubbery form is called the glass transition temperature, T g. A .
At the glass transition temperature, the physical nature of the material changes subtly. It goes from being a rubbery, flexible material at higher temperature, above the glass . A higher glass transition indicates less energy is required for the bonds of the glass to relax their strain. This is usually due to a slower cooling rate. In a slower cooling rate .
PAI and PBI show both excellent resistance toward creep. PEEK has good creep resistance at room temperature. However, the creep resistance at temperatures around 150°C decreases down to 8 MPa, since the glass transition . The glass transition temperature (Tg) is a key property that dictates the applicability of conjugated polymers. The Tg demarks the transition into a brittle glassy state, .
At temperatures much above the “glass transition temperature,” labeled Tg in Fig. 1, the rates are so fast as to be essentially instantaneous, and the polymer acts in a rubbery manner in . The glass transition temperature, Tg, is the temperature at which polymer chains can slide past each other without breaking. When a polymer is cooled below its Tg, it gets very hard and brittle; when it is heated above its .
A low-temperature curing grade with a cure time of less than 5 minutes at 80 °C has a glass transition temperature of about 140 °C. A specially designed resin has a glass transition .
In glass-ceramics, creep could become significant and may change the mechanical properties drastically near the glass-transition temperature (T g) of the residual glassy phase [10], [11]. In this study, the creep behaviour of a glass-ceramic joined ox/ox CMC was evaluated in bending load. Table 1 summarizes the thermal properties of Mg 65 Cu 25 Y 10 and Mg 85 Cu 5 Y 10 obtained by DSC. The glass transition and the crystallization temperatures are in reasonable agreement with previously published data [29], [30]. Fig. 2 shows an enlargement of the sub-T g region for the DSC traces of Mg 85 Cu 5 Y 10 (a) and Mg 65 Cu 25 Y 10 (b), where the glass . Depth sensing indentation is used here to investigate the viscous behaviour of a glass in a wide range of temperatures. A specific high temperature instrumented micro-indentation device was developed to perform creep indentation tests with several indenter geometries (spherical, flat punch and Vickers) up to 1100. °C with a maximum load of 15 N.. . . Mastering polypropylene’s glass transition temperature is more than a technical detail—it’s a key factor in enhancing product performance and sustainability. Gaining a deep understanding of this temperature helps in refining product design and improving overall functionality. Learn more for key insights and applications.
called viscoelastic behavior, not only above the glass-transition temperature Tg but also below Tg. Thus, it can be presumed that the mechanical behavior of FRP also depends on time and temperature even below Tg which is within the normal operating-temperature range. These examples have been shown by Aboudi et al. [1], Gates [2], Rotem et al [3].

the test for elementary teachers 197-200 is hard to pass
polymers
PAI and PBI show both excellent resistance toward creep. PEEK has good creep resistance at room temperature. However, the creep resistance at temperatures around 150°C decreases down to 8 MPa, since the glass transition temperature of PEEK is reached. The .gov means it’s official. . when the service temperature is lower than the glass transition temperature, the creep curve of the epoxy resin polymer model shows the classical macroscopic creep experimental curve, but the variation curve of the real strain with time only shows the first stage. However, when the service temperature is .
Creep is time dependent deformation under high stress/load at high temperatures. Diffusion of atoms in a grain is faster at high temperature which is why creep happens at high temperatures. T/F? It must be also considered that the test temperature is about 300 °C lower than the melting on-set temperature of the glass-ceramic and that a glass transition temperature of a possible residual glassy phase in this glass ceramic has never been detected (Fig. 4). Download : Download high-res image (88KB) Download : Download full-size image .means of a depth-terminated nanoindentation load ramp. We know from the viscoelasticity theory that creep, including its time dependence, is controlled in polymeric materials by the free volume available for molecular (segmental) motions.1–8 According to one explanation, around the glass transition temperature T
In the present study we used a SiOC glass free of segregated carbon, which was obtained upon pyrolysis of polysilsesquioxane particles in hydrogen atmosphere [16], [17], and subsequent densification by means of hot-pressing at high temperature.The compression creep experiments of the phase-separated sample indicate that at temperatures beyond 1000 °C its .
Higher activation energy of larger STZs in Cu–Zr–Al–Ti enables less flow units, which offsets the creep enhancement by the excess free volume with Ti addition. The deeper the pressed depth of the indenter, the more contribution of the STZ operation on creep deformation. . metallic glasses having high glass transition temperature (T g . High Tg PCB materials, known for their elevated glass transition temperatures, offer vital benefits for electronics in high-temperature environments. They provide improved heat resistance and stability for reliable performance in various industries, including electronics, telecommunications, power circuits, and aerospace, promoting user satisfaction, lead-free . INTRODUCTION. Conventional glass is a nonequilibrium material made by rapid cooling from the equilibrium or the supercooled liquid states. The kinetic glass transition occurs because the volume or enthalpy of the glass formers deviates from the equilibrium values because of reduced molecular mobility with decreasing temperature such that the material .
For this purpose, the enthalpy of polymerization reactions (sample mass of about 60 mg), the time or temperature at which the polymerization rate achieves a maximum (for a 1. to study polymerization kinetics and conversion of selected initial temperature of polymerization) and the selected bone cements; glass transition temperature, Tg, of the . Throughout this temperature ramp, the sample was subject to a constant force of 0.5 N, where the penetration depth of the probe in the sample was measured as a function of temperature. For the indentation creep tests, .
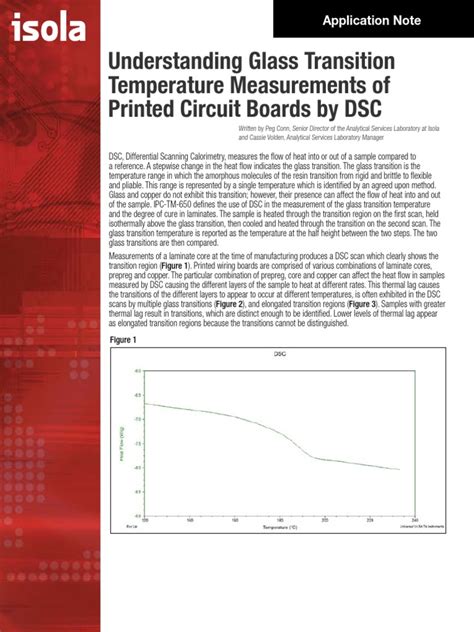
Glass Transition Temperature (T g) T g - Glass Transition Temperature for Epoxies TECH TIP 23 0-0.1-0.2-0.3-0.4-0.5-0.6 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 T g = 75ºC TEMPERATURE (ºC) HEAT FLOW (W/g) DSC Scan of a Typical Medium T g Epoxy Figure 1
Biopolymers are abundant, renewable, and biodegradable resources. However, bio-based materials often require toughening additives, like (co)polymers or small plasticizing molecules. Plasticization is monitored via the glass transition temperature versus diluent content. To describe this, several thermodynamic models exist; nevertheless, most . Glass transition temperature in nylons R. Greco and L. Nicolais* Laboratorio di Ricerche su Tecnologia dei Polimeri e Reologia de/CNR, Arco Felice (Napoli), Italy (Received 24 May 1976; revised 12 July 1976) The determination of the glass transition temperature of semi-crystalline polymers is a controversial problem in the literature, because of the complexity of .
Understanding the Glass Transition Temperature of
Below the glass transition temperature, the mechanical response is primarily influenced by secondary relaxation processes and excess configuration entropy, with activation volume increasing with strain. . which means that the relaxation event becomes less collective at higher stress. . Dynamic mechanical relaxation and thermal creep of high . An analysis of shift factor data for creep and SR experiments reveals two modes of molecular motion in the glass-rubber relaxation region, but the modes are less discernible than those reported .In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to undergo slow deformation while subject to persistent mechanical stresses.It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally .
"0 laminates exhibit a minimal amount of creep at low stress 6.2 MPa (900 psi) and moisture content (0.5-0.94 by mass) at room temperature". ". the major cause of creep of FRP comes from creep of the polymer matrix, creep of glass fibers is considered insignificant". 4 Creep III. Consider rule-of-mixtures to reduce creep Therefore, higher MW also has better resistance to (i.e., lower) creep and stress relaxation. Fillers and glass transition temperature – The effect offillers in polymers is usually a decrease in polymer chain mobility and an increase in the materials’ modulus; both cause lower creep and stress relaxation due to better resistance. For . Creep behavior of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) was investigated. HDPE has many engineering applications in different industries such as piping systems, cable and wiring, automotive parts . Using the nanoindentation technique, the creep deformation behavior of Zr55Co25Al15Ni5 bulk metallic glass (BMG) in the range of 0.94–1.03 glass transition temperature (Tg) and different loading rates was studied. The Maxwell–Voigt model was applied to describe the deformation and relaxation kinetics of BMGs near the glass transition. .
the test is hard

Resultado da Trilogy® Valor. View Photo Gallery. Get Email Updates. Save to Favorites. Request a Tour. 800-685-6494. Details. Floor Plan. Quick Move-In Homes.
high glass transition temperature means less creep|Glass Transition Temperature and Flatness — A Breakdown